For system, network and cloud administrators

There might be situations where you find yourself in need of creating, having a Windows MySQL server but you can’t actually install it. I found that it is better, more practical, efficient to have a portable Windows MySQL server version running on your hardware rather than one installed.
-
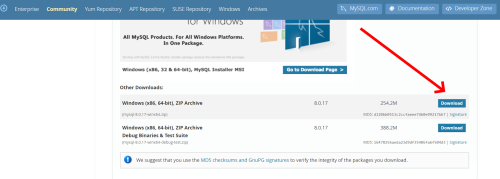
Download MySQL community server
You can just go ahead and download the latest MySQL community server archive. Make sure you’re looking for the .zip archive and not the Windows installer.
-
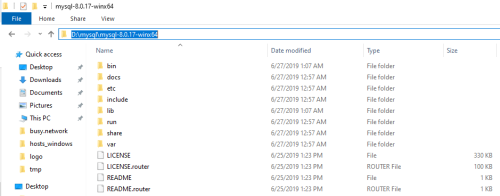
Extract/unzip the newly downloaded file
You need to establish a desired location on your PC where you can extract/unzip the MySQL server archive. For example, I chose my D partition (D:\\mysql\\mysql-8.0.17-winx64).
-
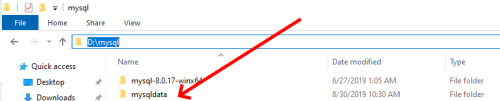
Create a mysqldata folder
It is recommended that you create a mysqldata folder for your MySQL server’s data files. It will help you a lot in the future, allowing you to backup and restore files anytime and however you want (my path is D:\\mysql\\mysqldata).
-
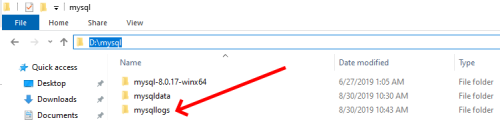
Create a mysqllogs folder
When running any kind of server (web, storage, databases, etc.), any admin will know that logging is a every important part of his job. Having a separate folder for your logs helps you manage and debug future problems (my path is D:\\mysql\\mysqllogs).
-
Create a options .ini file (recommended)
Even though as of MySQL 5.7.18, the Open Source community stopped including a options file my.ini file , I strongly recommend creating yourself a configuration file for the new MySQL server.
Microsoft Windows path names are specified in option files using (forward) slashes rather than backslashes. If you do use backslashes, double them.
Here’s an example of my.ini:
[mysqld]
sql_mode = NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
# the the installation folder
basedir = "D:\\mysql\\mysql-8.0.17-winx64"
# the folder where you've decided to create your data folder
datadir = "D:\\mysql\\mysqldata"
# if the server boots badly or doesn't like a particular change you brought into your MySQL server's code, telling the server what's the path to use when something needs to be logged (logins, sessions, changes, etc.) will ensure that you'll know where and what to look for when the server's security is being threatned
log-error = "D:\\mysql\mysqllogs\\error_0.err"
# the port number used for listening TCP/IP connections
port = "1212"
#OPTIONAL
# use this if you want to log changes to the binary log between backups
# server_id = "1"
# log_bin = "mysql-bin"
# configure your server in such a way that it starts using 70% of your RAM (for dedicated servers) or else 10%
# innodb_buffer_pool_size = 128M
# join_buffer_size = 128M
# you will need to experiment with the below settings and see which one fits bets for your server; current defaults are focused on fast SELECTs and transactions
# sort_buffer_size = 2M
# read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M
[mysqladmin]
#the user set for accesing your MySQL server
user = "root"
#the port used for accesing the administrative side of your MySQL server
port = "2323"
References used for testing and writing this article
- MySQL official community: Server Configuration defaults
- MySQL official community: Creating an Option File
- Sitepoint: How to install MySQL